多智能体(Multi-Agent)系统
引言
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用,以LLM为核心的Agent系统最近引起了广泛的关注。Agent(智能体)系统的设计旨在最大程度地利用LLM的归纳推理能力,通过为每个Agent分配明确定义的角色和任务信息,并为其配备相应的工具插件,以成功地执行复杂的任务。
当前主流框架主要专注于单一Agent的应用场景。在单一Agent的核心框架中,LLM与各种工具之间的协同作用至关重要。LLM通过深入理解用户任务的特征,推导出需要调用的工具,并基于这些调用的结果为用户提供实时反馈。在任务执行的过程中,Agent可能需要与用户进行多轮的交互以确保任务的准确执行。下图展示了单一Agent的组件架构,强调了LLM与工具的交互关系。
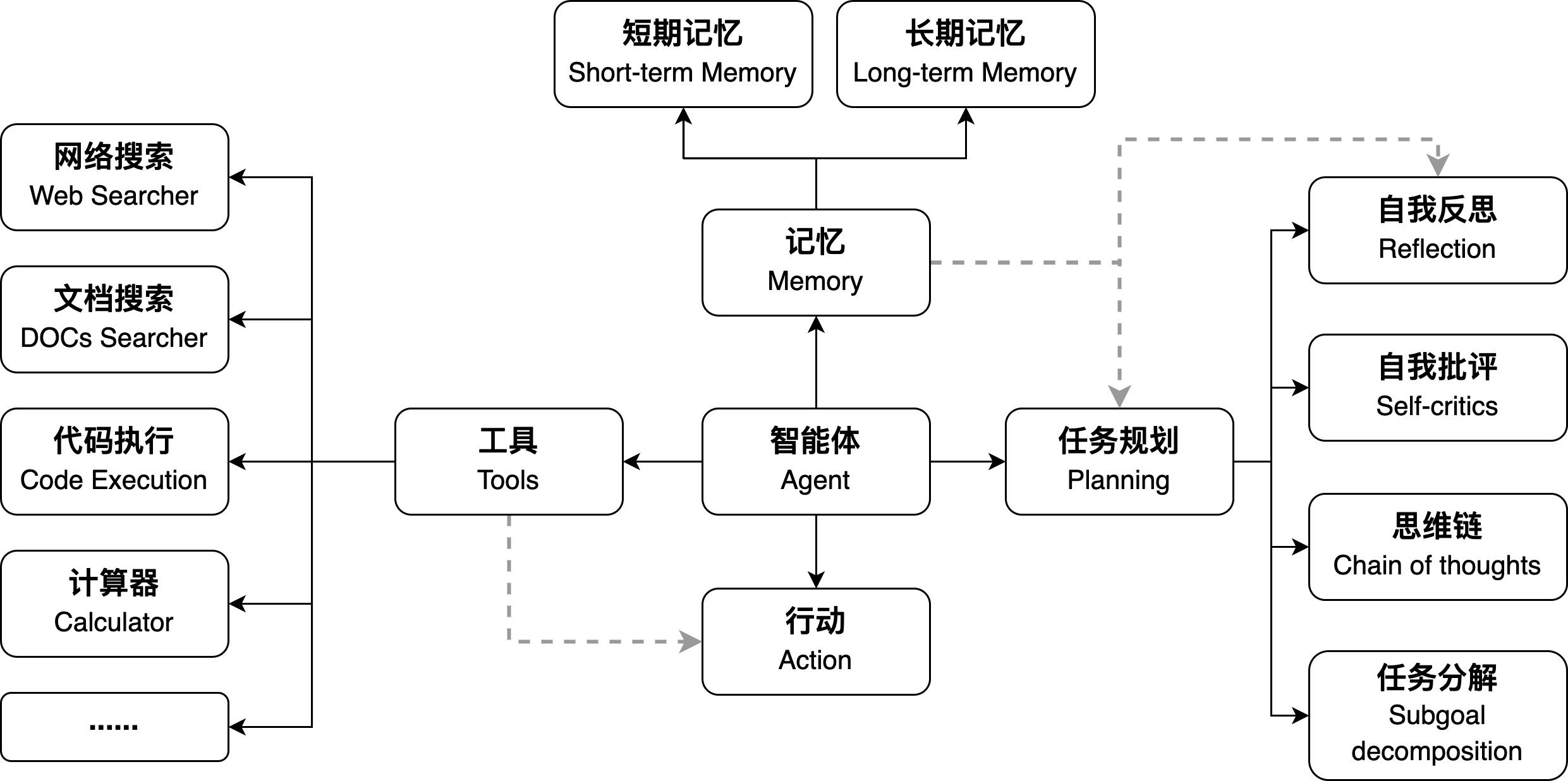
然而,单一Agent的设计存在一定的局限性,因此越来越多的Agent框架正专注于多Agent场景。在多Agent的背景下,多智能体系统通过为每个Agent明确定义独特的角色和任务定位,以及通过协同合作机制,成功地应对高度复杂任务的挑战。
多智能体系统
多智能体系统是由大型语言模型驱动,并以特定方式连接的多个独立智能体组成的复杂系统。每个智能体都配置有独立的提示词、大型语言模型(LLM)以及相应的工具。该系统的设计旨在促使不同智能体之间实现高效的协同合作,从而共同完成任务。通��过这种协同作业模式,系统为解决复杂问题提供了更为灵活和强大的解决方案。
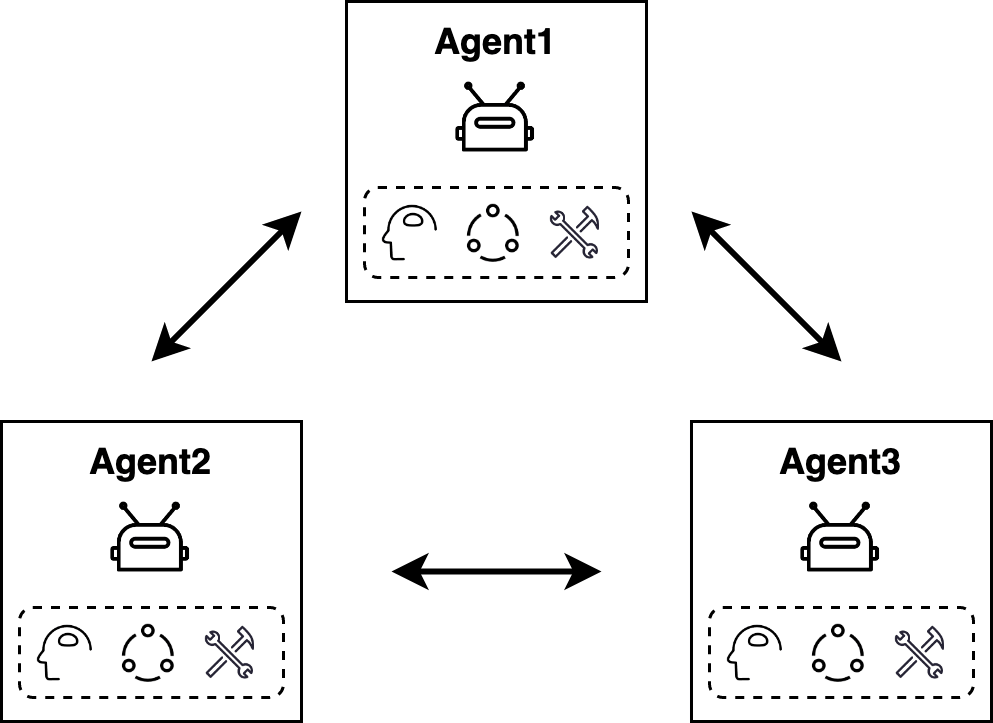
多Agent设计是当今复杂任务处理领域的一项关键策略,其优势不仅在于提高效率,还在于解决单一Agent面临的局限性。以下是多Agent设计的几个显著优势:
-
任务专注性: 多Agent系统的设计旨在使每个Agent能够专注于执行特定任务,以显著提升其在特定领域任务执行方面的质量,从而取得更为卓越的成果。
-
独立性: 系统中的每个Agent都被构建为独立实体,具备独特的提示、解释和few-shot示例。这种设计深化了对任务上下文的理解,同时增强了对提示的应用与理解能力。此外,系统结构赋予每个Agent独立进行微调、评估和优化的能力,使其能够在专业领域内展现卓越表现,进而提升整个系统的性能水平。
-
解决问题能力: 解决复杂问题通常需要综合多元的方法。在多智能体系统中,通过整合各个智能体的独特优势,提供了单一智能体难以比拟的全面解决方案。
-
灵活性和可维护性: 多Agent系统通过对每个智能体进行独立评估和优化的方式,确保了在提升单个Agent性能的同时,不影响整体应用的完整性。这种设计不仅增强了系统的灵活性,使其能够适应不同任务和场景,还提高了系统的可维护性,使其更易于管理和更新。
LangGraph简介
LangGraph是构建在LangChain之上,专为实现多智能体系统而设计的框架。LangChain采用链�式执行结构,遵循有向无环图(DAG)的设计原则。在处理复杂任务场景时,需要支持多个智能体(或角色)以循环方式协调执行任务。为了应对这一场景,LangGraph采用关系图和状态机(State Machine)的结合机制,使得智能体能够在一个循环的执行过程中被连续调用,直至任务最终完成。
LangGraph包含3个核心元素:
-
图状态(StateGraph)
StateGraph的主要职责在于存储图执行过程中的上下文关联信息和状态信息。在LangGraph框架的执行流程中,StateGraph负责在各个节点(Node)之间传递信息和状态。每个节点执行完毕后,StateGraph的状态将得到更新。 -
节点(Node)
节点(Node)在LangGraph中负责执行具体任务,每个节点都有一个名称(name),节点的值(value)则可以是一个函数(function)或者是一个Langchain LCEL中的Runnable可执行对象。此外,LangGraph定义了一个特殊的节点称为END,用于标识状态机的结束状态。 -
边(Edge)
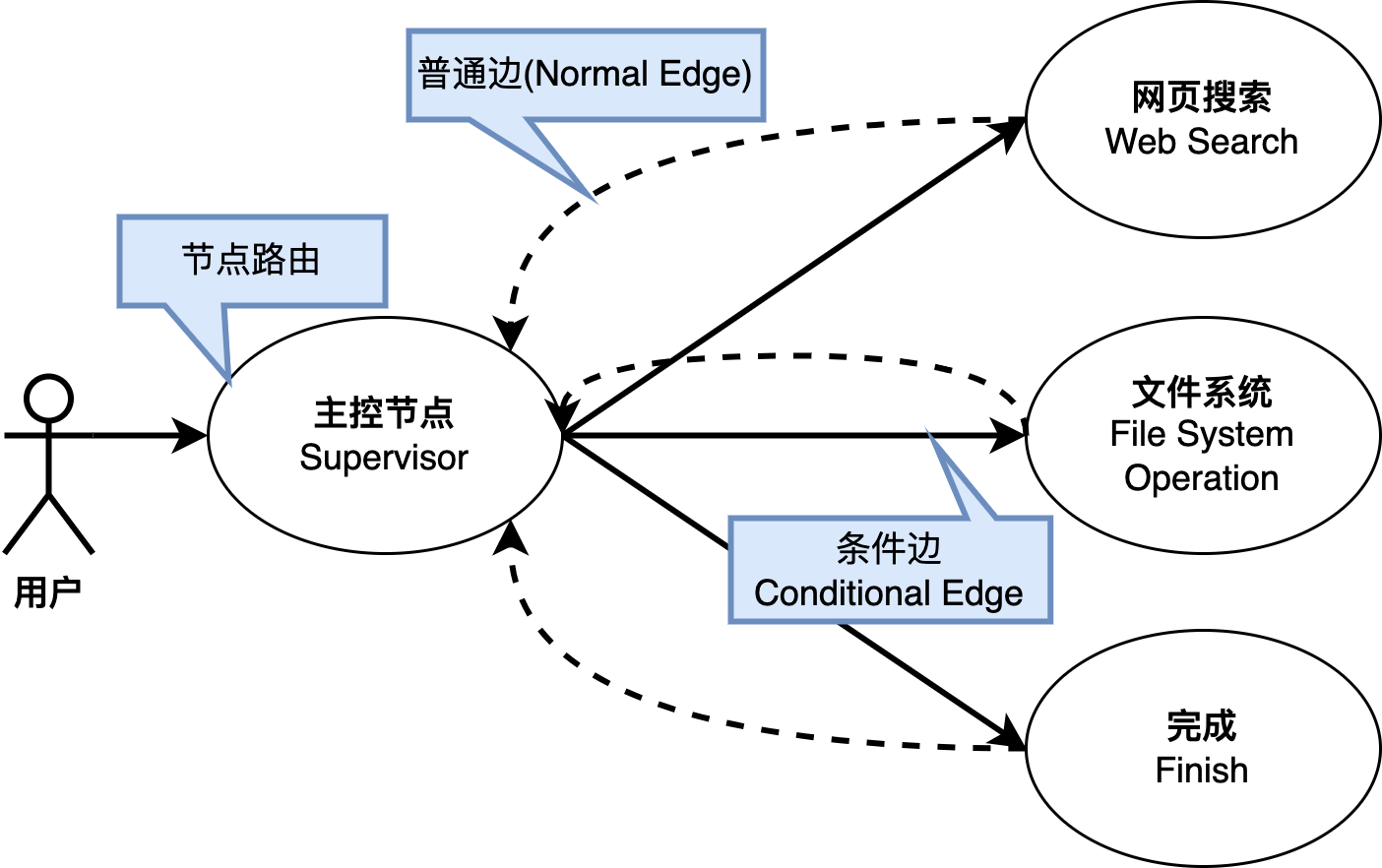
在图中,节点之间的关系通过边(Edge)来定义。LangGraph定义了两种类型的边:普通边(Normal Edge)和条件边(Conditional Edge)。
普通边(Normal Edge): 明确规定了两个节点之间的执行关系,上游节点将始终调用边(Edge)另一端的节点。
条件边(Conditional Edge): ,此类边则通过引入一个(路由)函数的概念,来动态决定下游节点的调用条件。
LangGraph多智能体示例
我们将演示一个基于LangGraph多智能体系统的简要示例,每个智能体都被指派执行独立的任务,以实现特定的功能。系统图包括三个关键节点:主控节点、网络搜索节点和文件目录操作节点。主控节点负责根据上下文相关消息来路由下一个执行节点和传递图状态,以协调这些智能体的协同工作。
代码实现
创建图状态
AgentState在此被用于存储两个重要状态。messages对象存储了系统在执行过程中生成的所有消息,next属性则被用于指示下一个即将执行的节点。
class AgentState(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], operator.add]
next: str
创建工具
这里初始化了2个工具:Tavily 和FileManagementToolkit。
Taily 是一个专为智能体(AI agents)设计的搜索引擎,特别针对检索式生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)目的进行了优化�。Tavily搜索API通过审查多个来源,从每个来源中找到最相关的内容,以便为大型语言模型(LLM)提供最优化的上下文环境。
FileManagementToolkit 是一个软件工具集专门用于执行各种文件操作,如复制、删除、移动和编辑文件。
tavily_tool = TavilySearchResults(max_results=1)
file_sys_tools = FileManagementToolkit(root_dir=str("./")).get_tools()
创建智能体帮助函数(Helper Function)
create_agent是一个便捷函数,专门用于快速创建智能体。一个智能体包括这些参数:一个大模型实例、提示词和工具。此函数接受三个关键参数:大型模型实例、提示词集,以及工具集合。这些组件共同为智能体提供了必要的能力和资源,包括信息处理、决策制定和执行特定的操作。
def create_agent(llm: ChatOpenAI, tools: list, system_prompt: str):
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
system_prompt,
),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="messages"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad"),
]
)
agent = create_openai_tools_agent(llm, tools, prompt)
executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools)
return executor
agent_node 函数用于基于智能体创建图节点对象。其主要责任是将智能体(Agent)的执行结果转换为HumanMessage。这些消息将作为重要的上下文关联信息存储在 StateGraph 对象中。
def agent_node(state, agent, name):
result = agent.invoke(state)
return {"messages": [HumanMessage(content=result["output"], name=name)]}
创建主控节点
在此我们创建了基于OpenAI Function Calling的链作为主控节点。函数调用是OpenAI GPT-4和GPT-3.5 Turbo模型的特性,允许这些模型根据用户提示决定是否�调用外部函数,增强了模型与外界环境的交互能力。
提示词指导ChatGPT扮演主控节点的角色,负责在各成员节点之间进行有效的路由。这一路由过程依赖于OpenAI的函数调用机制,通过此机制调用的函数能够返回一个名为next的变量,该变量内包含了下一步应执行节点的信息。
members = ["Researcher", "FileOperator"]
system_prompt = (
"You are a supervisor tasked with managing a conversation between the"
" following workers: {members}. Given the following user request,"
" respond with the worker to act next. Each worker will perform a"
" task and respond with their results and status. When finished,"
" respond with FINISH."
)
# Our team supervisor is an LLM node. It just picks the next agent to process
# and decides when the work is completed
options = ["FINISH"] + members
# Using openai function calling can make output parsing easier for us
function_def = {
"name": "route",
"description": "Select the next role.",
"parameters": {
"title": "routeSchema",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"next": {
"title": "Next",
"anyOf": [
{"enum": options},
],
}
},
"required": ["next"],
},
}
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system_prompt),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="messages"),
(
"system",
"Given the conversation above, who should act next?"
" Or should we FINISH? Select one of: {options}",
),
]
).partial(options=str(options), members=", ".join(members))
llm = ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key=openai_api_key,openai_api_base=openai_api_base)
supervisor_chain = (
prompt
| llm.bind_functions(functions=[function_def], function_call="route")
| JsonOutputFunctionsParser()
)
创建智能体和节点
在此,我们借助已经构建的工具和链创建了智能体。随后,我们以此智能体为基础建立了图节点。
research_agent = create_agent(llm, [tavily_tool], "You are a web researcher.")
research_node = functools.partial(agent_node, agent=research_agent, name="Researcher")
file_op_agent = create_agent(llm, file_sys_tools, "You are a file system operator, you can write content to a file.")
file_op_node = functools.partial(agent_node, agent=file_op_agent, name="FileOperator")
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
workflow.add_node("Researcher", research_node)
workflow.add_node("FileOperator", file_op_node)
workflow.add_node("supervisor", supervisor_chain)
创建节点和边关系
在此,我们为所创建的节点建立了图关系,这些关系分别是:
- 普通类型的边关系
这一关系通过使用add_edge方法添加,其中搜索节点(Searcher)和文件系统节点(FileOperator)与主控节点(Supervisor)之间建立直接连接。这表示一旦这些节点执行完成,流程将直接回溯至主控节点。 - 条件类型的边关系
这一关系通过使用add_conditional_edges方法添加,主控节点与搜索节点、文件系统节点以及结束节点之间形成条件类型关系。这意味着从主控节点进入这三个节点时,会根据图状态条件来判断选择哪一路径。
在成功创建边关系后,通过使用set_entry_point方法来指定此图的主入口节点为"supervisor"节点。
for member in members:
# We want our workers to ALWAYS "report back" to the supervisor when done
workflow.add_edge(member, "supervisor")
# The supervisor populates the "next" field in the graph state
# which routes to a node or finishes
conditional_map = {k: k for k in members}
conditional_map["FINISH"] = END
workflow.add_conditional_edges("supervisor", lambda x: x["next"], conditional_map)
# Finally, add entrypoint
workflow.set_entry_point("supervisor")
graph = workflow.compile()
执行任务
我们已多智能体系统提出一项任务,要求其执行以下操作:“搜索最新的Langchain新闻并将其记录到langchain-news.txt文件中”。
for s in graph.stream(
{
"messages": [
HumanMessage(content="find the latest langchain news and write to langchain-news.txt file.")
]
}
):
if "__end__" not in s:
print(s)
print("----")
我们观察到任务被分成了两个执行阶段。首先,主控节点协调搜索节点进行LangChain最新新闻的检索,并为所获新闻撰写了简明扼要的摘要。随后,主控节点将该摘要传递至文件操作节点,由文件操作节点负责将此信息写入langchain-news.txt文件。
{'supervisor': {'next': 'Researcher'}}
----
{
'Researcher':{
'messages':[
HumanMessage(
content='I found the latest Langchain news in an article titled "The Ultimate Guide To LangChain In 2024" on slashdev.io. The article discusses the features and capabilities of LangChain, emphasizing its power in crafting AI conversational systems that are responsive, intelligent, and adaptable across various domains and applications.\n\nI will now write a summary of this news to the "langchain-news.txt" file.\nSummary of the Latest Langchain News:\n\nThe latest Langchain news can be found in an article titled "The Ultimate Guide To LangChain In 2024" on slashdev.io. The article highlights LangChain\'s features and capabilities in crafting AI conversational systems that are responsive, intelligent, and adaptable across various domains and applications. LangChain is built on complex algorithms and machine learning models, enabling it to process and generate language with a human-like grasp of semantics and context. It offers a promising foundation for developers to drive the future of language models towards more dynamic and intuitive interactions between humans and machines.\n\nThis summary captures the essence of the latest Langchain news.',
'next': 'Researcher'
]
}
}
----
{'supervisor': {'next': 'FileOperator'}}
----
{
'FileOperator':{
'messages':[
[
HumanMessage(
content='The summary of the latest Langchain news has been successfully written to the "langchain-news.txt" file.',
'next': 'FileOperator'
]
}
}
----
{'supervisor': {'next': 'FINISH'}}
----
最终,输出文件内容如下:
Summary of the Latest Langchain News:
The latest Langchain news can be found in an article titled "The Ultimate Guide To LangChain In 2024" on slashdev.io. The article highlights LangChain's features and capabilities in crafting AI conversational systems that are responsive, intelligent, and adaptable across various domains and applications. LangChain is built on complex algorithms and machine learning models, enabling it to process and generate language with a human-like grasp of semantics and context. It offers a promising foundation for developers to drive the future of language models towards more dynamic and intuitive interactions between humans and machines.
This summary captures the essence of the latest Langchain news.